数据类型
1.数据类型有哪些?有什么差别?
8种数据类型
- 7种原始类型:Undefined、Null、Boolean、String、Number、Symbol(ES6)、BigInt(ES6)
- 1种引用类型:Object
原始类型和引用类型的区别
- 原始类型:值直接存储在栈中
- 引用类型:在栈中存储指向地址的指针,引用值存储在堆中,解释器通过指针地址,找到在栈中的值
2.Null和undefined有什么区别?
查看答案
| 定义 | 转数值类型 | |
|---|---|---|
| null | 空对象 | 0 |
| undefined | 未赋值的变量,对象未赋值的属性,函数没有返回值 | NaN |
3.数据类型检测方法有哪些?
typeof null、对象、数组都是object,无法使用typeof判断
typeof undefined // undefined
typeof null // object
typeof true // boolean
typeof ‘str’ // string
typeof 1 // number
typeof Symbol(1) // symbol
typeof 1n // bigint
typeof [] // object
typeof // object
typeof function() // function
A instanceof B:B是否在A的原型链上,只能判断引用数据类型(对象,数组,函数)
undefined instanceof undefined // Right-hand side of 'instanceof' is not an object
null instanceof null // Right-hand side of 'instanceof' is not an object
true instanceof Boolean // false
‘str’ instanceof String // false
1 instanceof Number // false
Symbol(1) instanceof Symbol // false
1n instanceof BigInt // false
[] instanceof Array // true
instanceof Object // true
function() instanceof Function // true
constructor属性:无法判断Symbol类型
true.constructor === Boolean // true
‘str’.constructor === String // true
1.constructor === Number // true
Symbol(1).constructor === Symbol // false
1n.constructor === BigInt // true
[].constructor === Array // true
().constructor === Object // true
(function()).constructor === Function // true
如果修改一个对象的prototype原型,则对象的constructor为prototype的类型
Object.prototype.toString.call() 完美办法
Object.prototype.toString.call(undefined) // '[object Undefined]'
Object.prototype.toString.call(null) // '[object Null]'
Object.prototype.toString.call(true) // '[object Boolean]'
Object.prototype.toString.call(‘str’) // '[object String]'
Object.prototype.toString.call(1) // '[object Number]'
Object.prototype.toString.call(Symbol(1)) // '[object Symbol]'
Object.prototype.toString.call(1n) // '[object BigInt]'
Object.prototype.toString.call([]) // '[object Array]'
Object.prototype.toString.call() // '[object Object]'
Object.prototype.toString.call(function()) // '[object Function]'
4.typeof null的结果是什么,为什么?
查看答案
typeof null; // object
- 因为null的类型标签跟object一样都是000
5.typeof NaN的结果是什么?
查看答案
number
6.判断数组的方式有哪些?
查看答案
[] instanceof Array
[].constructor === Array // 构造函数
Array.prototype.isPrototypeof([]) // 原型方法isPrototypeof()判断Array是否在数组的原型链上
[].__proto__ === Array.prototype // 数组的__proto__属性 = Array的原型
Object.getPrototypeOf(arr) === Array.prototype // Object.getPrototypeOf()返回指定对象的原型
Object.prototype.toString.call([]) === ‘[object Array]’
Array.isArray([])
7.类型转换的方式有哪些?
隐式类型转换: 运算符两边类型不同,js在计算中自动进行的类型转换
- 数字 加 字符串: 转字符串
- 数字 加 undefined/null/boolean: 转数字
- 数字 减/乘/除 字符串: 转数字
- 符串 加 undefined/null/boolean: 转字符串
- boolean 加/减/乘/除 undefined/null: 转数字(undefined转数字为NaN)
- 对象的加/减/乘/除: 转Object.prototype.toString.call(obj)
- 等于号、大于号、小于号的比较运算
强制类型转换: 手动调用全局函数来实现
- Number()
- Boolean()
- String()
- parseInt()
- parseFloat()
8.类数组转数组的方法
查看答案
- 使用call和apply方法改变this指向,再slice/splice/concat原型方法
- 使用Array.from转数组
- 使用...扩展运算符转数组
- 创建一个空数组,使用for...in遍历类数组的key/value
function foo(){
// Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments)
// Array.prototype.splice.call(arguments, 0);
// Array.prototype.concat.apply([], arguments);
// Array.from(arguments)
}
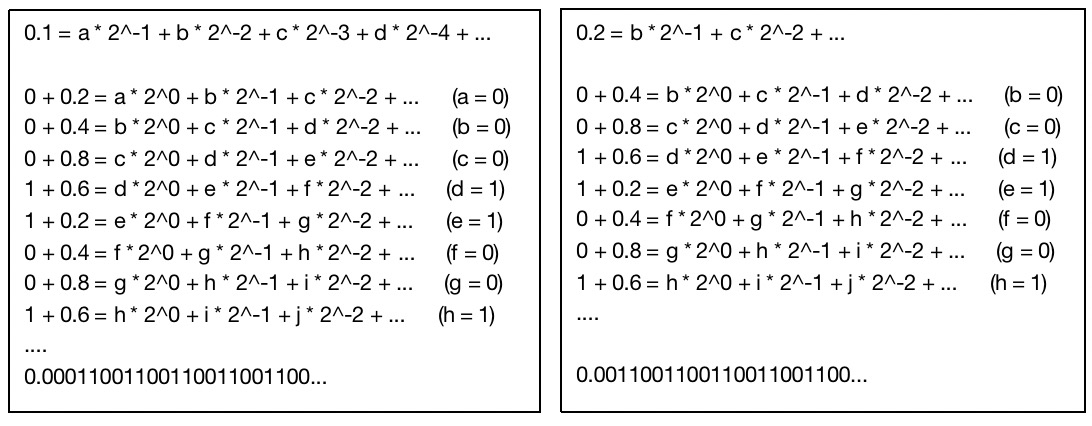
9.为什么0.1+0.2 ! == 0.3,如何让其相等现?浮点型精度问题的处理
查看答案
- 计算机中数据是通过二进制方式存储的,0.1+0.2两个数的二进制之和。0.1+0.2 = 0.30000000000000004
// Number.EPSILON属性判断两个值是否相等
function numberepsilon(arg1,arg2){
return Math.abs(arg1 - arg2) < Number.EPSILON;
}